Throughout the history of technology, we’ve witnessed the evolution of software applications—from massive monolithic servers to sleek microservices and miniaturized platforms. History, indeed, has a way of repeating itself, and Generative AI is no exception to this cyclical progression.
Today when you consume ChatGPT, Gemini, CoPilot the intelligence comes from the centralized computing:
Consuming Large Language Model
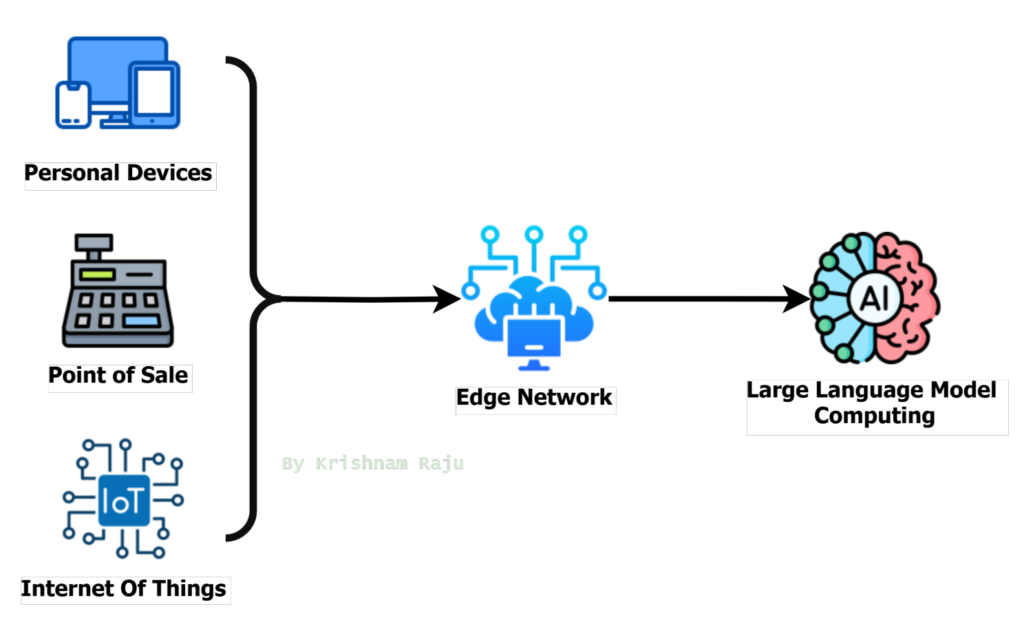
Now that you’ve delved into the realm of Large Language Models (LLMs), mastering techniques like Prompt Engineering and Retrieval-Augmented centralized intelligence Generation (RAG) patterns, it’s time to shift gears. The focus is no longer on centralized intelligence, but rather on bringing AI-driven capabilities closer to customers or end user devices.
With the devices limitation we could not deploying LLM intelligence directly on the devices. Now comes the rise of SLM (Small Language Models), which are built for everyday use.
The Rise of SLMs in Everyday Use
From powering smarter mobile applications to revolutionizing real-time translations and beyond, small language models are quietly shaping our digital lives. Developers and researchers are increasingly favoring SLMs for their ability to deliver lightweight yet impactful solutions.
What are Small Language Models?
Inherently, Small Language Models (SLMs) are smaller counterparts of Large Language Models. They have fewer parameters and are more lightweight and faster in inference time. We can consider models with billions and trillion of parameters as LLMs (the largest Chat GPT-4o: has 1.8 trillion parameters), demanding resource-heavy training and inferences. The definition of a Small Language Model can vary among different authors.
How are they different from LLMs?
Unlike large language models (LLMs), with primary purpose of general-purpose capabilities across a variety of applications, SLMs are optimized for efficiency, making them ideal for deployment in resource-constrained environments such as mobile devices, point of sale, IOT and edge computing systems.
SLMs are compact versions of Language Models, and they excel in two main areas:
- SLMs are suitable for Edge Devices, offering businesses benefits such as cost reduction, offline usage, or enhanced data privacy.
- SLMs facilitate speeding up R&D progress, swiftly testing new ideas, benchmarking at scale, and iterating relatively fast. Even retraining SLMs (even from scratch) is feasible for small groups with access to home-grade GPUs.
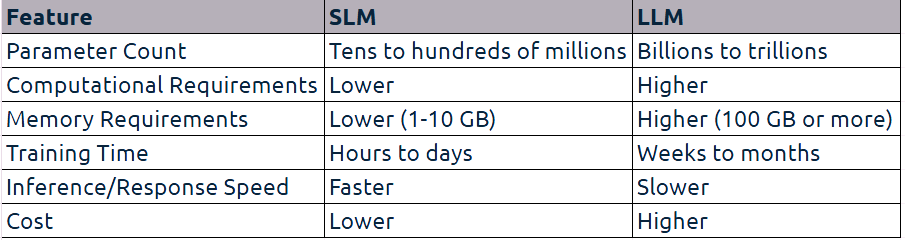
SLM (Small Language Model) vs. LLM (Large Language Model) Comparison:
Small Language Models (SLMs) are designed for efficiency and specialization, making them ideal for a variety of use cases across industries. Here are some notable applications:
- Real-Time Mobile Apps
- Customer Support: SLMs can power chatbots and virtual assistants on websites or apps, providing instant responses to customer queries.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyze customer feedback from social media and integrate insights into customer data platforms.
- Personalized Offers: Generate tailored promotions and recommendations based on user profiles and behavior.
- Self-Healing Systems: SLMs can enable networks to automatically detect and resolve issues without human intervention.
- Edge Computing
- IoT Devices: SLMs enable smart home devices, like thermostats or speakers, to process commands locally without relying on cloud servers or choking the internet.
- Connected Cars: They can assist with navigation, voice commands, and diagnostics directly within the vehicle.
- Domain-Specific Applications
- Retail: SLMs can enhance Point-of-Sale (POS) systems by offering personalized recommendations or promotions.
- Finance: Used for fraud detection, transaction analysis, and customer service in banking apps.
- Privacy-Sensitive Environments
- Data Masking: SLMs can anonymize sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- On-Device Processing: By running locally, SLMs reduce the need to send data to external servers, enhancing security.
- 5. Specialized Content Creation
- Marketing: SLMs can generate targeted ad copy or social media posts for specific audiences.
- Technical Writing: Used to create concise and accurate documentation for niche industries.
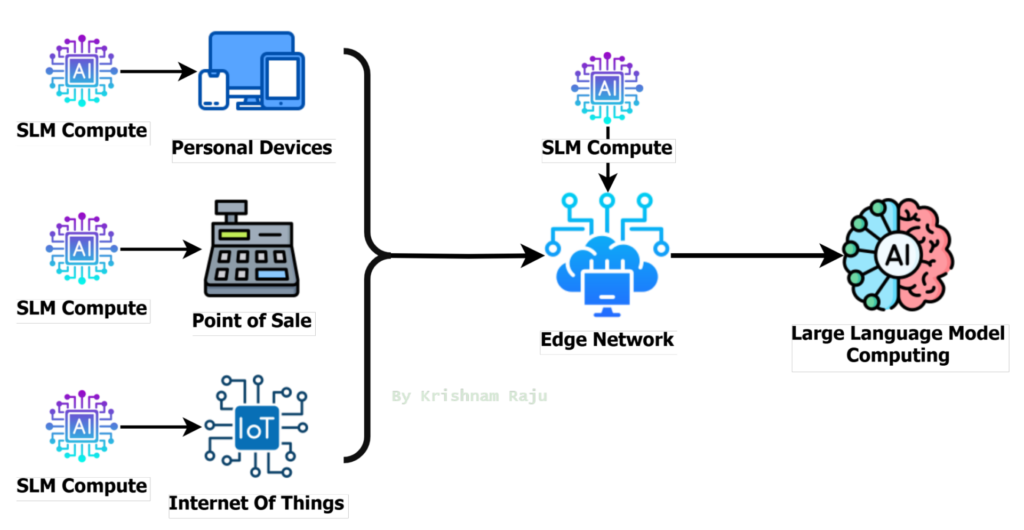
Now let’s redraw the same image with SLM, the compute can be deployed on every entry with specific customizations:
Customized Small Language Model’s for Specific Use Cases
Conclusion
Small Language Models (SLMs) are revolutionizing the way we think about AI—bringing the power of intelligent computation closer to end users. They are compact, efficient, and purpose-built to address specific use cases across industries, from retail and IoT devices to connected vehicles and telecom.
By processing data closer to the edge, SLMs not only reduce latency but greatly improve privacy and accessibility, making them the future of responsive, on-device intelligence. As we continue to innovate and adapt these models, the possibilities for seamless integration, improved customer experiences, and optimized operational efficiencies are boundless.
The future of AI isn’t just large-scale intelligence—it’s small, smart, and specialized. Let’s embrace this next frontier.
Article Written by Krishnam Raju Bhupathiraju.